*** Please read the latest on the Type 218SG here. ***
RSN's Silent Service
The Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) had been operating conventional diesel-electric submarines since 1995. Initially, as it was a completely new capability for a small navy, the RSN opted to purchase 5 decommissioned / used submarines from Sweden. These were the A-11 Sjöormen class submarines first commissioned in the late 1960s. Four of these boats were re-commissioned as the Challenger class and the fifth was to be salvaged for parts. They were extensively refurbished and upgraded by Kockums for use in tropical climate and came with personnel training agreements with the Royal Swedish Navy. They form the 171 Squadron based at Changi Naval Base.
The Challenger class submarines enabled the RSN to learn the trade of undersea warfare in an accelerated timeframe but they had one glaring shortcoming - they were not equipped with air-independent propulsion (AIP). AIP is simply an advanced underwater propulsion system in a non-nuclear submarine that did not involve access to atmospheric oxygen, eliminating the periodic need to surface or snorkel to recharge the batteries. ( see my previous blog AIP submarines for RSN )
In 2005 an opportunity to buy another 2 decommissioned submarines from Sweden came in the form of two A-17 Vastergotland class boats. These were a generation newer than the Challenger class boats, having been launched in 1986 and 1987. They were extensively modified and had their hulls sliced and lengthened to accommodate a proprietary Stirling AIP engine. They were eventually commissioned as the RSS Archer and RSS Swordsman.
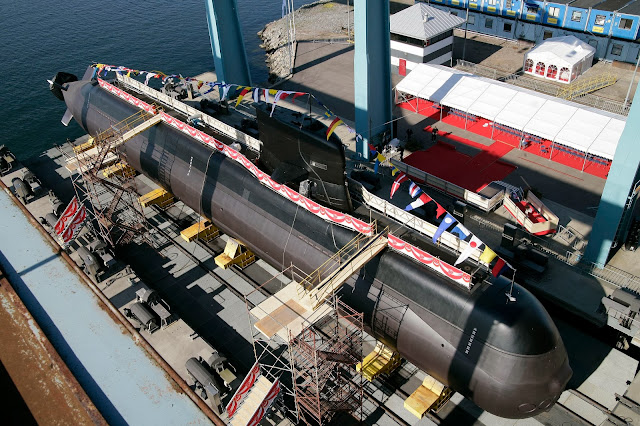 |
| RSS Archer during her launching ceremony in Sweden in June 2009. Source : Peter Nilsson Kockums AB. |
 |
| The Stirling Conversion : From Vastergotland to Archer. Kockums picture |
Submarine Shopping
Now that the submariners have honed their skills with AIP, it is time for the RSN to consider buying more potent and newer platforms. On 2nd Dec 2013 MINDEF made public the acquisition of 2 customized AIP capable submarines from ThyssenKrupp Marine System GmBH (TKMS). From the MINDEF press release " These submarines, together with the Archer class submarines, will replace the ageing Challenger class submarines. The Challenger class submarines were built in the 1960s and will be progressively retired from service. The replacement submarines will have significantly improved capabilities and be equipped with Air Independent Propulsion systems." With some background information, it would not be of too much a surprise that this time it would no longer be a Swedish design.
Boat Supplying Nations
There are not many countries that have the capability to design and build submarines. The United States have not looked back on conventional diesel-electrics ever since they commissioned the world's first operational nuclear submarine the USS Nautilus (SSN-571) in 1954. The Royal Navy similarly disposed off their Upholder class SSKs and are and all-nuclear force. What's left will be Germany, with their U-209s and U-214s, probably the largest exporter of conventional submarines in the free world, France, the supplier of Scorpenes, Spain, exporting their S-80 Scorpene variant, Sweden, with their ill-fated Collins-class project but enjoying better domestic success and in exporting to Singapore, and finally Russia, with the Project 636 improved Kilo class. Japan is just beginning to come online as a potential supplier, after ditching their post WWII pacifist Constitution. South Korea builds U-209s and U-214s under licence and exported a couple to Indonesia, and China builds but hardly exports. All said, if you are buying U-boats ( presumably non-nuclear ), your options are somewhat limited. If you are sourcing for nuke boats then your choice is simple, go to Uncle Putin, but be warned, you can get badly mauled like India did with its yet to be delivered INS Vikramaditya ( ex-Admiral Gorshkov ) carrier.
The Boote Yards
Kockums AB's Karlskrona shipyard has been producing first rate submarines for Sweden since the 1912. Apart from the A-11 Sjöormen class and the A-17 Vastergotland class SSKs already mentioned above, they also constructed three A-19 Gotland class submarines with air-independent propulsion for the Swedish Navy in 1990. Their next generation offering is the A-26 submarine, originally scheduled to replace the Vastergotlands as they are retired in 2020.
In a series of miscalculations by the Swedish government, the fortunes of Kockums began to change around the turn of the century (1999 to be precise) where, in a complicated web of industrial merger and acquisition, Celsius AB sold its subsidiary Kockums AB to German ship builder Howaldtswerke-Deutsche Werft GmBH (HDW) in an all-share swap for 25% of HDW, with an option to exit the business with a lump sum. The following year, SAAB bought over most of Celsius AB and opted to be paid and exited. And so Kockums become a part of HDW and then HDW was itself acquired by ThyssenKrupp Marine System GmBH (TKMS) in 2005.
HDW is of course most famous for submarines - their U-205, U-206 and U-209 series conventional diesel-electric submarines are in active service in many navies all around the globe, not to mention the Dolphin Class variant for the Israeli Navy. Their latest offering is the U-212A and its export version the U-214.
TKMS is a huge German conglomerate and in addition to Kockums which it acquired through HDW, owns several other shipyards in Germany and Greece. It now has two competing lines of submarines to sell in a limited post-cold war global market and the number of submarine exports are just not enough to keep the yards busy. It does not help when many customers also insist on local construction and technology transfer. It just not possible to maintain both the German HDW and Swedish Kockums to compete against its rivals like DCNS of France and Rubin Design Bureau of Russia. Understandably TKMS would favour its German shipyards over the other foreign ones.
So when the time came for Singapore to replace her Challenger class submarines, Kockums, the exclusive supplier of submarines to the Republic of Singapore Navy for the past 18 years saw its monopoly broken and was prevented from submitting a bid by its parent company. Instead, TKMS offered HDW's U-218SG, to be built in its Kiel shipyard in northern Germany.
On a separate note, TKMS had also successfully stalled Kockum's next-gen A-26 AIP offering to the Swedish government which industrial insiders believe is delayed by contract negotiations between Kockums and Sweden's Defence Materiel Administration. The two parties simply cannot come to a price agreement.
Fortunately, this impasse may be about to change as Singapore's HDW purchase had finally whipped the Swedes into action to ( forcefully? ) buy back Kockums and regain control of their submarine building capability and put the A-26 acquisition back on tract. In what has come a full circle, on 29th Jun 2014 SAAB announced that it will buy Kockums back from ThyssenKrupp for SEK 340 million ( about USD 50.5 million) in a deal that is probably subsidized by the Swedish government. Still, the U-218SG purchase is a done deal and the A-26, severely undermined by ThyssenKrupp, will never be ready by 2020 even for its domestic client, the RSwN.
The Mysterious U-218SG
All that we know about this submarine is that it is a customized design for Singapore. It is a conventional diesel-electric hunter-killer submarine with air-independent propulsion based on HDW's current designs, due for delivery in 2020. No other information is available in the public domain about this new boat. Unless you have insider information, right now everything is speculation.
Still, there is nothing to stop anyone from making an intelligent guess as to what this new submarine would turn out to be. A good start will be to understand Singapore's operational requirements and the currently available HDW U-boats designs.
The U-218SG will likely be involved in the following :
Anti-surface and anti-submarine operations
Special forces deployment
Unmanned vehicle deployment ( UUV and UAV )
Land attack missions with cruise missiles
Intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition and reconnaissance ( ISTAR )
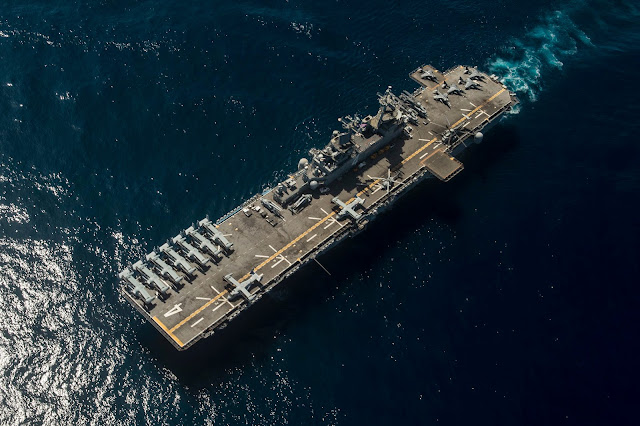
Carrier battle group ( CVBG ) escort - future Endurance-160 type large helicopter / F-35B carrier
Singapore's existing Challenger and Archer class SSKs are in the 1200 to 1400 ton range and are really too small to cope with all of the above functions. Even the existing HDW options, the Type 212A built for the Deutsche Marine ( German Navy ) and the Marina Militare ( Italian Navy ), as well as the export version the Type 214 are all in the 1500 to 1700 ton range.
Unlike European navies who operate in the relatively smaller and shallower Baltic Sea, the Mediterranean Sea, North Atlantic Ocean and the North Sea, those in the Indo-Pacific region including Japan, South Korea, India and Australia would probably require bigger submarines with much longer range. The main role of the U-218SG will surely not be to play cat and mouse with the RMN in the narrow Straits of Malacca. It might have a bigger role in maintaining the SLOC open in the South China Sea and beyond, given the aggressive behavior of China in recent years. So it has to be bigger with a longer range and endurance. It also has to be faster, at least as fast as the carrier task group that it is supposed to protect. A bigger submarine will also have more space for more comfortable crew accommodation.
Fortunately HDW has exactly such a design concept in the form of the Type 216 AIP weighing in at 4000 ton. This is a double hulled two decked ocean-going monster was designed to fulfill the requirements for the Australian SEA 1000 Collins replacement project. However, it would be too big for the RSN if the design is adopted at face value. It would never safely transit the congested waters of the Straits of Singapore without being observed ( or bumped into )! So perhaps 2500 to 3000 tons would be a good compromise. A scaled down U-216 while retaining all the original bells and whistles. There is precedence in the Project Delta frigates - the Formidable class being an improved but smaller version of the La Fayette class stealth frigate.
 |
| The HDW U-216 SSK Source : ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems |
Length : approximately 90m
Pressure Hull Diameter : approximately 8.1m
Surface Displacement : about 4000 tons
HDW Fuel-cell Air-Independent Propulsion System
Lithium-Ion Polymer Battery Technology
HABETaS rescue system for personal rescue / free ascent at 300m
Endurance : 80 days at sea. 4 weeks without surfacing.
Range : 10000 nautical miles
Compliment : 33 officers and ratings. Extra capacity for divers and attached personnel
IDAS fibre-optic guided missile system for defense and attack against aerial targets ( ASW helos included )
Weapon Tubes : 6 x 533mm ( torpedoes, anti-ship missiles, mines, UUV? )
Vertical Launch System : Vertical Multi-Purpose Lock for launching cruise missiles
Torpedo Countermeasure System
Special Forces Swimmer Delivery Vehicle ( SDV )
In other words - the works. All that anybody could ask for in a submarine short of SLBM launch capability.
 |
| The innovative Interactive Defence and Attack System for Submarines (IDAS) is a
lightweight fibre-optic guided missile for submarines against aerial threats.
Photo : ThyssenKrupp Marine Syatems |
 |
The MdCN ( Missile de Croisiere Naval ) or naval cruise missile can be
launched from the torpedo tubes of a submarine. Source : MBDA
|
 |
The MdCN, aka naval SCALP, can also be launched from the
A70 Sylver vertical launch system of France's FREMM frigates. Source : MBDA |


















.jpg)














